ICSE 2025 – Chemistry Paper
Maximum Marks: 80
Time Allowed: Two hours
General Instructions
Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes.
This time is to be spent in reading the question paper.
The time given at the head of this Paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
Section A is compulsory.
Attempt any four questions from Section B.
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ].
Section A (40 Marks)
(Attempt all questions from this section. Do not copy the questions. Write the correct answers only.)
Question 1
[ Atomic weight: C=12, H=1]
S + 2H₂SO₄ → 3SO₂ + 2H₂O
Reason (R): The most reactive metal is at the top of Group 1.
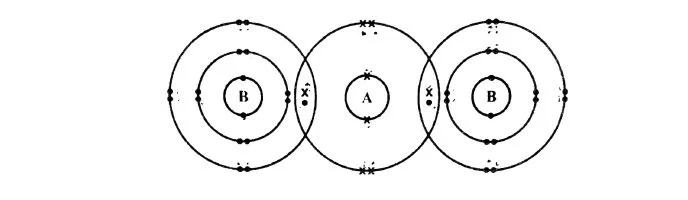
Which option represents correct electronic configuration of atoms A and B before combining together to form the above molecule?
Reason (R): Dense fog or misty droplets of sulphuric acid are formed which are difficult to condense.
Cl-, Li+, Al3+, K+
Identify the pair of ions which have the same electronic configuration:
(Atomic numbers: Cl = 17, Li = 3, Al = 13, K = 19)
Which statement about the electrolysis is NOT correct?
The equation of the reaction is given below:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
All volumes are measured in room temperature. What is the total volume of gases remaining?
Question 2
(i) A student was instructed to prepare and collect ammonia gas using aluminium nitride. The student set up the apparatus as shown below. Study the given diagram and answer the following questions. [5]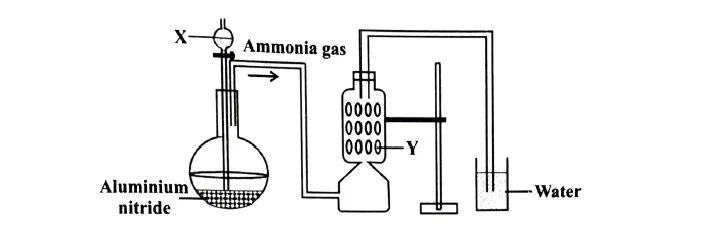
(ii) State the terms for the following: [5]
(iii) Complete the following sentences by choosing the correct words from brackets. [5]
( Ag → Ag⁺ + e⁻ / Ag⁺ + e⁻ → Ag )
(iv) Match the Column A with Column B: [5]
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| (a) N2 + 3H2 ⇌ 2NH3 | 1. Vanadium Pentoxide |
| (b) 4NH3 + 5O2 → 4NO + 6H2O | 2. Nickel |
| (c) 2SO2 + O2 ⇌ 2SO3 | 3. Iron |
| (d) CH4 + H2 → C2H6 | 4. Concentrated Sulphuric Acid |
| (e) CuSO4·5H2O → CuSO4 + 5H2O | 5. Platinum |
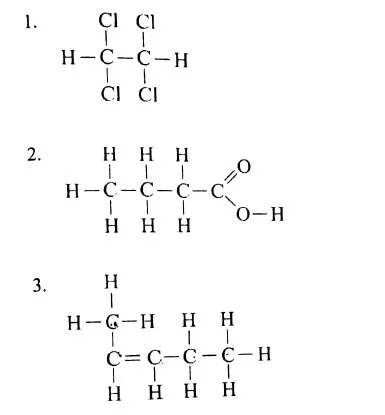
(v) (a) Draw the structural diagram of the following organic compounds: [5]
(b) Give IUPAC name of the following organic compounds:
Section B (40 Marks)
(Attempt any four questions from this Section.)
Question 3
(i) The atomic number of two atoms X and Y are 14 and 8 respectively. [2]State:
- The period to which X belongs.
- The formula of the compound formed between X and Y.
(Do not identify X and Y)
- Anode is known as the oxidizing electrode.
- Graphite electrodes are preferred in the electrolysis of molten lead bromide.
(iii)The reaction between concentrated sulphuric acid and magnesium can be represented by the equation given below: [3]
Mg + 2H2SO4 → MgSO4 + 2H2O + SO2
If 60 g of magnesium is used in the reaction, calculate the following:- The mass of sulphuric acid needed for the reaction.
- The volume of sulphur dioxide gas liberated at S.T.P.
(Atomic weight: Mg = 24, H = 1, S = 32, O = 16)
- A solution of barium chloride is added to zinc sulphate solution.
- Lead nitrate is heated in a test tube.
- Chlorine gas is passed over moist starch iodide paper.
Question 4
(i) A gas cylinder can hold 150 g of hydrogen under certain conditions of temperature and pressure. If an identical cylinder with the same capacity can hold 450 g of gas G under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, find:[2]
- The vapour density of the gas G.
- The molecular weight of gas G.
(ii) Complete and balance the following equations:[2]
- CH3COONa + NaOH
??CaO→
- CH3COOH + Mg → ?
(iii) Name the gas produced during each of the following reactions: [3]
- When copper is treated with hot, concentrated nitric acid.
- When ammonia is burnt in an atmosphere of oxygen.
- When ferrous sulphide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
(iv)Study the table given below. Use only the letters given in the table to answer the questions. Do not identify the elements. [3]
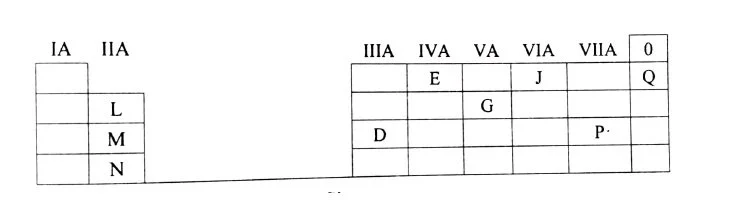
- State the valency of element G.
- Which element can exhibit catenation?
- Write the formula of the compound formed between M and P.
Question 5
(i) Given below are two sets of elements from two different periods: [2] Name the element with the highest ionisation potential in each of the following sets.
- Al, Cl, Mg
- Ne, O, F
(ii) Ammonia gas is passed over heated copper (II) oxide in a combustion tube: [2]
- Name the gas evolved.
- What will be the colour of the residue that is left in the combustion tube at the end of the reaction?
(iii) Give balanced equations for the following: [3]
- Action of dilute hydrochloric acid on ammonium carbonate.
- Oxidation of sulphur with hot concentrated nitric acid.
- Reaction of concentrated sulphuric acid with carbon.
(iv) Rohit took two different salt solutions in test tubes C and D as shown in the figure below. [3]
He added dilute HCl to each of the two test tubes. The products formed in the test tubes C and D are silver chloride and lead chloride respectively.
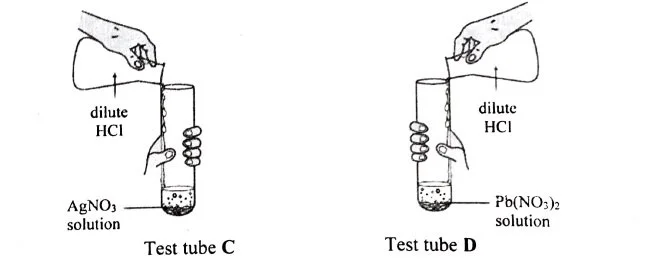
- State one common observation made by Rohit in both the reactions.
- State the observations made by him on addition of excess of ammonium hydroxide to the products formed in:
- Test tube C
- Test tube D
Question 6
(i) Given below is a diagram showing the placement of five different oxides. With respect to the given diagram, answer the following questions:[3]
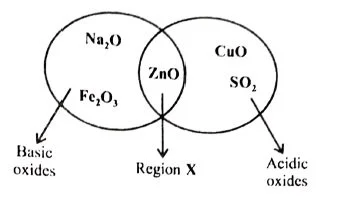
- Name the type of oxide represented in region X in the diagram.
- Identify the oxide which has been incorrectly placed in the above diagram.
- Name the oxide from the above diagram which will form an alkali when dissolved in water.
(ii) Given below are organic compounds labelled A to F.[3] Answer the questions that follow:
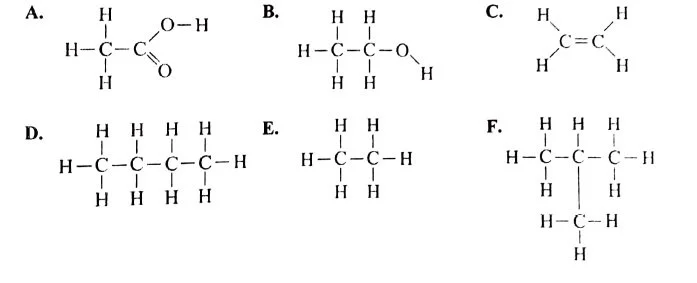
- Which compound forms a single product with bromine?
- Which two compounds have the same molecular formula?
- Which two compounds will react together in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to form a product with a fruity smell?
(iii) An organic compound ‘X’ contains carbon, oxygen and hydrogen only. The percentage of carbon and hydrogen are 47.4% and 10.5% respectively. The relative molecular mass of ‘X’ is 76.Find the empirical formula and the molecular formula of ‘X’ .[4]
[Atomic weight: C = 12, O = 16, H = 1]Question 7
(i) Seema added a few pieces of copper turnings to a test tube containing concentrated acid P and she noticed that a reddish-brown gas evolved.[2]
- Name the acid P used by Seema.
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction that took place.
(ii) Answer the following questions with reference to the concentration of bauxite ore. [2]
- Name the process used to concentrate the ore.
- Give a balanced chemical equation for the conversion of aluminium hydroxide to pure alumina.
(iii) Draw the dot and cross structure of the following: [3]
- An ionic compound formed when Mg reacts with dilute HCl.
- A covalent compound formed when H2 reacts with Cl2.
- The positive ion produced when ammonia gas is dissolved in water.
(Atomic number: Mg = 12, Cl = 17, H = 1, N = 7)
(iv) Acidulated water is electrolysed using platinum electrodes.[3]
- Why is dilute sulphuric acid added to water?
- Write the reaction taking place at the cathode.
- What is the observation at the anode?
Question 8
(i) [2]
- State Avogadro’s Law.
- Define Co-ordinate bond.
(ii) Differentiate between the following pairs of compounds using the reagent given in the bracket:[2]
- Ammonium chloride and Sodium chloride (using an alkali)
- Zinc Nitrate solution and Calcium Nitrate solution (using excess sodium hydroxide solution)
(iii) You are provided with some compounds in the box.[3]
PbO, CH4, HCl, PbO2, NCl3, SO2, CO2
Choose the most appropriate compound which fits the descriptions (a) to (c) given below: [3]
- A colourless gas which turns acidified K2Cr2O7 from orange to green.
- A yellow explosive oily liquid formed when excess chlorine gas reacts with ammonia gas.
- A yellow metallic oxide formed on thermal decomposition of PbCO3.
(iv) P, Q, R, S are the different methods of preparation of salts: [3]
- P – Simple displacement
- Q – Neutralisation by titration
- R – Precipitation
- S – Direct combination
Choose the most appropriate method to prepare the following salts:
- PbCl2
- FeCl3
- Na2SO4
